Common diseases of goat and sheep
There are various kinds of common diseases in sheep and goats. Who knows, I or you will experience one of these diseases of goat and sheep.
All farmers would want to have no livestock that has a disease. But, if it turns out fate says otherwise, we already know and are ready for anticipation.
Ok, let’s get started.
Sheep and goats are livestock that are easy to raise.
Goats and sheep of all types, the population is spread evenly throughout the world.
Either in large or small numbers, raising goats or sheep can be beneficial.
The proof, there are goat and sheep breeders who have only 1 tail, 2 tails, 5 tails to hundreds or even thousands. After all, which amounted to 1 or two tails still keep sheep.
Goat farming is beneficial because of its potential. Because every business everywhere there is a risk.
In my opinion, minimizing that risk lies in the management of the livestock. Manage, care for and care for goats and sheep.
In this post, I will try to write about an important part of the management diseases of goat and sheep , namely about the diseases most encountered by small ruminant animals such as goats and sheep.
Diseases that can infect goats and sheep are due to infection and non-infection.
Goat and sheep diseases due to infections such as diseases due to viruses, bacteria, and parasites.
While goat and sheep diseases due to non-infectious causes such as bloating and poisoning.
Disease of Goat and sheep due to virus
Goat and sheep diseases caused by viruses, for example, are Orf and Bluetongue.
Orf, if I’m not mistaken, like the scab and bluetongue, the tongue turns blue.
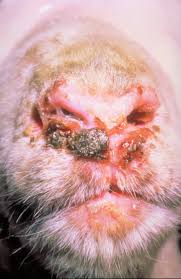
The symptoms of goats affected by orf are blistered goatskin. Because this orf often attacks the mouth of the goat, so the blister is usually around the mouth of the goat.
Viruses that cause orf in goats and sheep can be contagious and are zoonotic.
Zoonosis is an infecting virus that can attack humans too. So, we must be quite vigilant about this virus.
If the ORF attack is in the mouth of a goat, then the goat will usually have difficulty eating.
So sorry … because it’s hard to eat, goats will become thin. If the goat is thin, it’s also a pity for the breeder.
Orf Symptoms in goats and sheep
The first symptom of this orf is the appearance of red spots appearing on the skin of the goat. Usually at the base of the lips.
These red spots gradually become vesicles. In medical terms, vesicles are defined as blisters and fluid-filled skin.
Flakes of goat or sheepskin that have a liquid become pustules. This pustula is a blister but the contents are already in the form of pus.
If the disease has reached this stage, it will usually become crusty and stiff, making it difficult for goats or sheep to eat.
If the disease spreads, the area of the crust can become wider.
Parts of the goat’s body that are often attacked are the mouth and face, stomach, legs, testicular sacs, udders, nipples, and vulva.
Favorite animals that are attacked by orf are goats and sheep. Of the other ruminant animals, goats and sheep are the animals most easily attacked by the orf virus.
Although it does not rule out animals such as deer, camels and dogs can be attacked by this orf. The severity of infection from this disease can be small to fatal.
The severity of the outbreak of this virus is between 2.2 – 100%. So, there is still a big possibility, that the goat or sheep is still able to recover.
Goats or sheep are healed, so they will become immune to this virus. This immunity takes about 1 year after the goat recovers.
However, this immunity is not passed down to young goats.
For example, goats or ewes recover from orf and become pregnant and have children. This kid only inherits a small part of its mother’s immunity. If there is an orf attack that is quite severe, it is likely to still be infected.
Orf disease can be transmitted from sick goats/sheep to other goats/sheep in direct or indirect contact.
Indirectly the disease is contagious due to contact between healthy goats and materials, tools or environment contaminated with orf virus.
The way the orf virus enters into the body of a goat is through small wounds such as scratches that occur on the skin due to sharp grass, thorns or cuts due to other things.
Urgent!!!
Orf disease is caused due to infection by a virus. So, medical treatment only has a slight effect.
Effective action is to prevent and provide vaccination to healthy goats/sheep. Goats and sheep that are infected with orf can be given antibiotics to prevent secondary infections.
Goats and sheep are also given a multivitamin to maintain body condition.
On the infected skin, softening ointments can be given to help the mouth of the goat/sheep not be too sick at mealtime. A local ointment that can be used is iodine tincture.
Goats/sheep that are attacked by orf need to be fed soft food so that the goat/sheep can eat well and sufficiently so that the condition does not deteriorate.
Thus, the immune system will be better at resisting disease.
Besides Orf, the disease experienced by goats and sheep due to viruses is Bluetongue.
This virus is transmitted through the Colicoides sp.
Goats or sheep that are infected by this virus can experience a fairly high mortality rate.
Symptoms of this disease are the goat or sheep will experience a high fever, the saliva will melt, the face and tongue will swell, and the tongue of the goat or sheep is bluish.
In the next stage, the goat or sheep will experience inflammation in the nails, so that the goat when walking will use its knees.
Goat disease due to bacteria
Anthrax is a disease caused by bacteria that can infect goats and sheep.
This disease is included in the category of dangerous diseases. The name of the bacteria is Bacillus anthracis.
This disease can be transmitted to humans. Humans can become infected when in contact with animals affected by anthrax, through meat, bones, skin, or feces.
Even so, until now there have been no cases of humans contracting through touch or contact with people who suffer from anthrax.
Symptoms of anthrax goats and sheep are that goats and sheep experience bleeding that comes out of all body holes and sudden death in livestock.
Goat disease due to parasites
Goat diseases caused by parasites include scabies, diseases of the digestive tract and liver worm disease.
Scurvy in goats and sheep caused by Sarcoptes scabei infection often attacks goats or sheep.
This scabies causes scab sores on the skin throughout the body.
Goats or sheep become agitated because of itching, decreased appetite, thin if the disease is very severe and not treated immediately can cause death.
This disease is very contagious to other animals and also to humans.
The parasitic gastro-intestinal nematode worm, which attacks small ruminants such as goats and sheep, is Haemonchus contortus.
This disease can cause symptoms of diarrhea, decreased appetite and thinness in goats or sheep.
Meanwhile, the trematode worm parasite, Fasciola hepatica, can cause severe liver damage to goats or sheep.
The symptoms are not very visible, but loss of appetite and thinness in goats.
If the disease has been going on for a long time and the liver damage has spread, the animal can die suddenly, and at post mortum, the liver is damaged and many adult worms are found.
To make it easier to understand, I will make a list of these goat and sheep diseases.
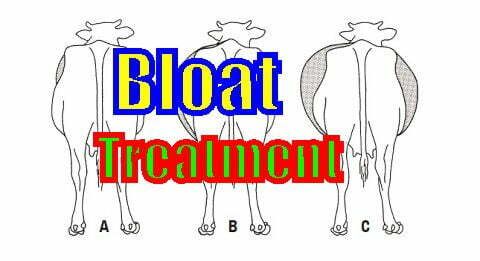
1 . Bloated Goat
Symptoms arise when gas in the rumen cannot get out because the rumen fluid is covered by foam from the fermented feed in the rumen.
In these conditions, the gas formed can suppress internal organs including the heart and lungs so that death can occur.
Signs of a bloated goat initially lose appetite, the left abdomen will harden, and bulge.
After that, the goat will shortness of breath, stiff legs (straight) and bleating so hard that it makes you shocked.
Then, DEAD.
Causes of bloated goats include:
- Bloating in goats can be caused by eating too much-wet forage.
- Rumen bloating often occurs when animals consume large amounts of legumes.
- Eating too much concentrate.
Therefore, prevention can be done by:
If the goat is grazed, the time is not too early. At least until the dew dries. Maybe around 10 o’clock. If the goat bloats when grazing and not monitored, the goat can die on the spot.
Taking grass or forage after rain, it should not be given immediately. At least wait until the water is gone from the feed. For example, when you take forage in the afternoon, it is given in the morning or when you take it in the morning, give it in the afternoon or evening.
The cause of bloated goats is due to legumes and concentrates, it is because the amount of protein eaten by goats is excessive. Don’t give both types of feed too much at once.
To be safe, a distance of one hour after the goats eat legumes or concentrates, goats are given forage with higher crude fiber. For example Napier grass, banana leaves and field grass.
How to treat bloated goats.
Grasp the front leg of the goat.
Massaging the left belly of the goat.
Give the goat to drink coconut oil.
Goat anus hole entered by papaya leaf stalks (smear oil so slippery).
If you surrender, call a medical officer or butcher.
2 . Wormy goat and sheep disease
Worms in goats are due to parasitic attacks from outside. That is, goats eat larvae or worm eggs in the feed.
As a result, worms will live and develop in the goat’s digestive tract. To support their lives, worms take nutrients from goats so that goats become malnourished.
Overcoming parasitic worms is very necessary. Because the first step before a new goat enters the cage is to clean this parasite.
Symptoms of goats that are worms are:
- the goat becomes weak.
- Thin
- slow growth
How to treat it is to provide worm medicine. Many sell this worm medicine. Usually, the active ingredient contained in it is albendazole.
Treating worms needs to be done periodically. Because it does not rule out the goat will eat worm larvae again.
3 . Diarrhea in goats
Diarrhea in goats indicates that there is a problem with goat digestion. The cause can be due to various things. 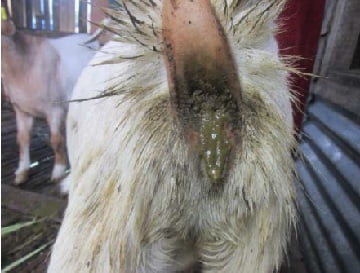
- Less sterile goat feed.
- Goat kid drinks contaminated milk replacer.
- Changes in the environment, changes in diet.
- Infections due to bacteria, this causes food or rations to be unsterile.
- Goat food is less fiber. Goats that eat too much-wet food can cause diarrhea. There are cases of goats that are given too much rice bran without forage compensating for diarrhea.
Treatment for goat diarrhea is:
Give the goat a drink with a mixture of salt and minerals. Do not let the goat become dehydrated.
Improve good and sterile eating patterns. Namely, by providing fibrous feed.
If diarrhea doesn’t stop, the goat has likely been infected by parasites from outside.
The treatment can be injected with broad-spectrum antibiotics. For example wormectin.
4 . Scabies
Diseases of goat and sheep caused by Sarcoptes scabei infection often attack goats and sheep.
This scabies causes scab sores on the skin throughout the body. Scabies is a goat skin disease that often occurs.
Goats or sheep become agitated because of itching, decreased appetite, and thin if the disease is very severe and not treated immediately can cause death.
The signs of this scabies disease are goats or sheep experiencing itching, skin scabbing, hair loss in the infected area and at an advanced stage, the skin can thicken.
Scabies or scabies can be transmitted easily through direct contact, and materials in a cage such as a fence, feedlot, and other materials that have been contaminated by this disease.
Treatment of scabies in goats
If scurvy has not been much, we can treat it ourselves with simple ingredients.
First, the scabies is cleaned with antiseptic fluid on the goat’s body. For example refanol or 70% alcohol.
If possible, the hair around the scabies is scraped off to make it easier to administer drugs.
Then, spread scabies with finely crushed sulfur mixed with used oil.
The point is, we kill the bacteria that cause these scabies first. If the source of the disease is dead, these scabies will gradually disappear by itself.
Don’t forget to separate the affected goat from other goats. This disease is contagious.
If scabies has spread widely to the goat’s body, then the most effective treatment is to inject with parasitic drugs. For example ivomec or wormectin.
5 . Orf disease
Orf is different from scabies even though the symptoms look the same. If scabies is caused by bacteria, this virus is caused by a viral infection.
What we need to know is that the favorite animal of this orf is a goat.
I have written about this orf disease at the beginning of this post.
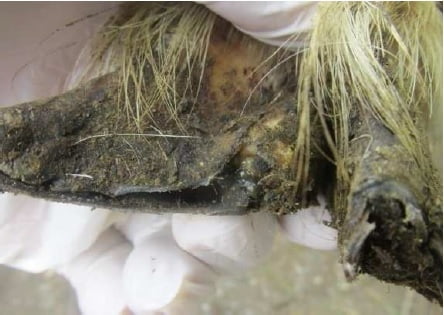
6 . Rotten nails
Nails are the first to support the weight of the goat. If the nails grow lengthwise and are not cut, the growth becomes irregular.
Thus, this can cause the weight support to shift slightly and cause injury to the base of the nail. When the cage is wet or not sterile, this can lead to infection by bacteria.
The Bacteria are very happy with the humid and wet environment. If this condition continues, it can cause rotten nails.
The goat will experience pain in its legs. When walking, the goat becomes lame and sometimes cannot stand.
Treatment of rotten nails
Goat nails are cleaned and cut to their normal shape.
After that, clean it with an antiseptic so that the bacteria will die.
So that no more infections, give antibiotic ointments or other types of antibiotics.
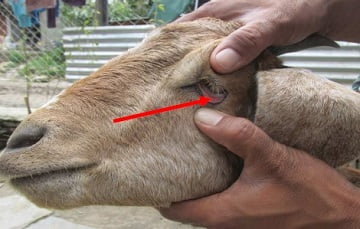
7 . Pink eye
Pink eye disease is sometimes known as brittle. This disease is caused by bacterial infections of Chlamydia psittaci ovis and Mycoplasma conjunctivae.
Bacterial infections are usually caused by an eye injury. Initially, it can be triggered by a cage environment with poor lighting, poor air ventilation so that it is very beneficial for bacteria to develop.
Symptoms of this disease are initially red-eye goats. Then eventually – the color of the eyes will become blurry.
Goats that suffer from pink eye will be sensitive to sunlight. So, if the goat is in a bright place the eyes will runny.
This disease can spread to other livestock. The transmission medium is direct contact or carried by insects such as flies.
Rarely are there pink eye cases that cause the goat to die. But it can cause blindness in goats, from temporary to permanent blindness.
Treated immediately.
How to treat it is to separate the goat who is sick with pink eye.
Then, clean his eyes with warm water, then apply special eye ointment for goats that contain antibiotics.
The provision of ointment is done 3-4 times a day to prevent secondary infections.
Antibiotics can inhibit or kill bacteria that cause infection. If the appetite of goats is still good, God willing, it will heal quickly.
8 . Anemia
If you see the goat is weak and lethargic, but there is no visible disease, it could be that the goat has anemia.
To check whether the goat has anemia or not, the way is as follows.
Look at the goat eye membrane.
- If the color is pink to red, the goat is fine.
- The color is pink, so the goat is still healthy.
- The color is pale pink, the goat has anemia.
- Pale color, no pink, severe anemia.
9 . Goat Poisoning
Poisoning in goats can be caused by the goats eating poisonous food or indeed goats accidentally eat forage that has just been sprayed with dangerous chemical drugs.
How to safely give poisonous cassava leaves for goat.
The reaction of the goat to this poisonous material is usually very fast.
On average, poisoned goats will experience convulsions, foaming mouth, bluish mucous membranes, and feces mixed with blood.
Handling poisoning: give Norit tablets or young coconut water. We can also give drinks from a mixture of coconut oil, young coconut water, salt, and tamarind. If poisoning by insecticide, drink 1 cup warm coconut milk.
10 . Anthrax
This anthrax disease is caused by a virus. This is not like an ordinary viral infection, but an anthrax attack is an epidemic.
This virus can kill goats quickly and in large quantities at the same time.
An anthrax goat will experience:
- High fever
- Limp body
- Respiratory disorders
- Swelling of the thyroid gland,
- full body boils,
- indigestion.
- Bleed from the ears, mouth, and anus.
Until now there has not been found a cure for this anthrax virus.
What can be done is communal control. That is farmers around the anthrax zone simultaneously prevent livestock from leaving the area.
If a livestock has been infected, the body is burned.
11 . Mastitis
Mastitis is an infectious disease in goats that attacks goat udder areas. This infection is caused by Staphylococcus Aureus bacteria.
The reason is less sterile milking management or incomplete goat milking process.
This incompleteness will be a good medium for the development of bacteria. This can cause the udder of the goat to become swollen.
The treatment is by giving intra-mammary antibiotics, which are antibiotics that are injected directly into the goat udder.
For mastitis cases not to occur again, good and sterile milking management must be applied.
12 . Myiasis
Myiasis is a disease in goats that have maggots. Sometimes this wound can make a hole in the goat’s muscle tissue. Inside the hole is a maggot.
This myiasis can be triggered due to an open wound on the goat’s body. Then the fly flies and is used to lay the eggs of the fly.
When these eggs develop, the larvae consume the goat’s body tissue.
The most common cases are open sores that are neglected and goats that have given birth.
A goat that has given birth will leave a lot of blood sticking around the anus and thigh. If not cleaned, this can invite flies to nest there.
The way to treat it is we have to kill and remove the larvae of these flies. Namely, by spraying antiseptic fluid into the wound area.
This antiseptic liquid can be refanol, alcohol, spiritus, or other branded products. It can be obtained easily at the farm store.
After the maggots are all out, the wound can be smeared with antiseptic and covered with gauze.
If the covered process is not possible, spraying with an antiseptic must be done frequently so as not to invite flies to come again.
13 . Nail and Mouth Disease
Usually caused by Aphthae Epizootica (AE) found in urine, milk, and saliva.
Clinical symptoms: decreased appetite, fever, excessive salivation, oral cavity, tongue and foot blisters and there are lumps filled with clear fluid.
The infected goats are separated and treated, keep the cage clean and vaccinate.
14 . Pneumonia
This disease can be caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, and unfavorable environmental conditions.
Examples due to environmental influences are humid, cold, dirty air and poor hygiene care.
Symptoms of this disease are:
- Decreased appetite.
- Having a fever and a cough.
- The goat has difficulty breathing or breathing too fast.
Keep the cage or fence so that it is not damp, always clean, not flooded, close the cage if the wind is strong and quarantine the sick goat. Treatment that can be done is to provide antibiotic preparations.
15 . Constipation or constipation
This disease is rarely experienced by adult goats. Because if the cause is due to lack of fluids, actually this has been resolved.
This is because when goats are thirsty, they don’t want to eat. They will bleat until they get drinking water.
Usually, most constipation is only experienced by newborn goats.
The first goat kid feces, usually black, thick, and hard so it is difficult to get out.
Goat is affected by constipation in addition to hard to poop, he will also roll around and bleat frequently. So, to launch a bowel movement, one tablespoon of vegetable oil can be given.
16 . Enterotoxemia
Caused by eating excessive seeds. This can make Clostridium Perfringens bacteria in the rumen more productive. Due to its acidity, it produces toxins that are detrimental to the goat.
Clinical symptoms: goat twitching, fever, until the teeth crunch and swollen stomach.
This disease can be prevented by annual vaccinations, especially goats that are breastfeeding and not giving too much grain in the feed.
17 . Botfly Larvae Parasitic Infection
This is almost the same as myiasis. Namely, there are open sores whose contents are fly larvae.
This botfly fly is different. The size of the fly is bigger. The bite is very painful and immediately results in open wounds (blisters).
Very often these flies interfere with PO cows, but do not rule out the possibility that goats can also be targeted.
After a bite scar occurs, they will return until they succeed in laying their eggs.
If this egg succeeds in hatching on the goat’s body, it will become the larvae that eat away the goat’s meat.
The treatment is the same as myiasis.
18 . Liver Worm Infection
Liver worms are caused by the type of Fasciola Hepatica worm.
This parasite can attack goats and live in the hearts of goats. Usually, this worm enters the goat’s body through the grass it eats.
Because the target is the heart, so this is more dangerous.
The treatment is the same as the worm disease above. But using a broad-spectrum drug, which can be used for all types of worms.
That’s the 18 goat and sheep diseases that are usually often experienced. Half are very often found by goat breeders.
 JOYNIM FARM Goat Farming, Cattle Farm, Laying Hens, Quail Farm, Gardening
JOYNIM FARM Goat Farming, Cattle Farm, Laying Hens, Quail Farm, Gardening