Rabbit urine as fertilizer is using rabbit drops and urine as plant nutrition. Be it solid or liquid excrement. Rabbit urine as fertilizer has no less good quality than other organic fertilizers.
Collect your rabbit urine and drop
Don’t just throw away the urine and solid feces. It can be accommodated, who knows someone is looking for it.
Because apart from the meat, rabbits can also be benefited from their feces. Especially the urine. being said, the urine is good as fertilizer. We’ll see, really good or just rumors.
Although rabbit urine production is not as much as goat and cow, rabbit urine has a higher economic value.
The price of rabbit urine is high, it could be because the goods are good, but the quantity is not much. So, the price is high.
It’s like that. Because only 10 adult rabbits can collect 2 liters of urine per day.
This means that per rabbit only produces about 200 mL of urine per day. While cows can be up to 5 liters per head of urine per day.
If you want to collect 10 liters per day, you can count the number of rabbits yourself.
The figures above are only estimates. Because the urine production of animals such as cows and rabbits is very much determined by the amount of drinking water, feed water content, and temperature.
To be able to collect rabbit urine, inevitably maintenance must be done in the battery cage.
Then under the floor of the cage, a gutter is installed that can collect and drain the resulting urine.
But the side effect, the cage must be smelly. Because urine and solid feces will be scattered on the gutter. If it is on the ground, this urine will be absorbed so that the odor can be reduced.
Must be cleaned every day. So that the organic N from rabbit urine does not turn into ammonia and can harm the health of the rabbit itself.
How to clean it can be sprayed with Nitrobacter probiotics. Because this Nitrobacter can convert ammonia into nitrites and nitrates which no longer smell.
Water that flows from spraying with Nitrobacter can also be collected again. Because the presence of nitrates is a good source of N for plants.
Rabbit Urine Composition
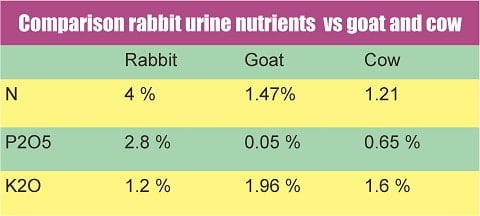
The nutrient content of rabbit urine is the highest compared to goats or cows.
But the compensation is the meager production. Meanwhile, the production of cows or goats is more with poorer nutrients.
According to a scientific publication, the content of liquid organic fertilizer derived from rabbit urine has a fairly high nutrient content, namely N 4%; P2O5 2.8%; and K2O 1.2% is relatively higher than the nutrient content in cattle (N 1.21%; P2O5 0.65%; K2O 1.6%) and goats (N 1.47%; P2O5 0.05%; K2O 1.96%). [1]
If only the rabbit was as big as a cow, the rabbit breeder would get rich quickly. Unfortunately, rabbits are created small, tiny, and cute.
What I mean is let’s count how many nutrients can be produced. For cows and rabbits.
The assumption is that rabbits produce urine 0.2 liters or 200 ml/head/day and cows 5 liters/head/day.
| 0,2 liters rabbit urine | 5-liter cows urine | |
| N organic | 0.008 | 0.06 |
| P2O5 | 0.0056 | 0.0325 |
| K2O | 0.0024 | 0.08 |
The amount of nutrients produced is still larger per cow.
Indeed, this comparison is not fair, because the size is very much different.
Therefore we can compare how many rabbits are kept to produce the nutrient equivalent of one cow.
For element N, one cow is equivalent to 7.5 rabbits.
While the phosphate element, one cow is equal to 5 rabbits.
The amount of potassium requires more rabbits, which is about 33 rabbits.
At least by raising 10 adult rabbits, we can get the same amount of liquid fertilizer as a cow. But with less urine volume.
In other words, the nutrient concentration is more intense.
But there are other scientific sources that say that the nutrient content in rabbit urine is not as much as the above. [2]
The number is lower. Can be seen in the table below.
| Nutrient content in rabbit urine | |
| N | 2.72 % |
| P2O5 | 1.1 % |
| K2O | 0.5 % |
Not only two but there is also still one more source that mentions the nutrient content of rabbit urine.
The value is even less than the two above. Rabbit urine contains nitrogen from 1.20 to 1.90%, phosphorus from 0.29 to 0.55, and potassium as much as 0.44 to 1.67%.
The latter illustrates that the urine content of rabbits is no different from the urine of other livestock.
Even the urine of a goat or sheep is higher than that of a rabbit.
Which one do you keep on?
This is confusing. Because the nutrient content contained in rabbit urine is influenced by the type of feed it eats.
The higher the protein content of the feed, the higher the nutrients in the urine.
Research that has been done, shows a brief result as in the table below.
Effect of feed on urine nutrient concentration in rabbits [3] | ||||
| Grass | River Tamarind | yam | Ipomoea Aquatica | |
| Nitrogen | 0.1 % | 1.7 % | 0.6 % | 0.9% |
| Phosphor | 10.23 ppm | 10.33 ppm | 21.9 ppm | 8.77 ppm |
| Potassium | 58.7 ppm | 107.87 ppm | 99 ppm | 51.45 ppm |
Lamtoro is a type of legume feed with a very high crude protein content.
The problem that occurs is that all livestock on average is now given concentrate for their feed.
Not only rabbits, cows, even goats, and sheep are also given concentrate feed.
The concentrate has a high crude protein content. Then the potential for rabbit urine containing high N is also great.
Like that approx. To be sure, laboratory test.
Rabbit urine as Foliar fertilizer
Rabbit urine as fertilizer can be used directly for plants. Without the need to add probiotics or any inorganic fertilizers, it will naturally become fertilizer.
But to increase its N value. The addition of probiotics is very possible.
It is necessary to be careful in choosing probiotics. And the treatment must also be correct. If it is wrong, it can make the quality of rabbit urine fertilizer messy.
Here are the steps or how to make rabbit urine fertilizer by adding probiotics.
The tools and materials that need to be prepared are rabbit urine, EM4, brown sugar, agricultural lime (dolomite).
The amounts of these ingredients are 1 liter of urine, 45 mL EM4, 4.5 grams of brown sugar, and 9 grams of agricultural lime.
Mix the ingredients above, stir until dissolved then ferment for 4 weeks.
According to research, the results and quality of liquid organic fertilizer from rabbit urine are as follows.
Rabbit urine organic fertilizer nutrient content[4] | |
| PH | 6.63 |
| C-Organic | 2.4 |
| Nitrogen | 2.26 |
| C/N ratio | 1.06 |
In the results above when compared to unfermented rabbit urine, there is a significant increase in the N value.
Because when compared to anaerobic fermentation for 2 weeks, the value of the N content is only 1.76%.
Because it uses EM4, the fermentation process does not need to be aerated. This is because most of the bacteria that act on EM4 are anaerobic.
If you do aeration, what works is the aerobic bacteria that have been in rabbit urine.
In addition, aeration will increase the pH of liquid fertilizer.
Even though the ones that work are aerobic bacteria, these bacteria will still break down organic N and use it for reproduction.
With the right fermentation time, this can produce rabbit urine fertilizer with a higher N value.
However, if allowed to continue, when the sugar runs out, the bacteria will start using N itself. This means that the N in fertilizers can be used up or reduced.
The point is that EM4 will not work if it is aerated in fermentation. This is not nonsense, as the data below will explain everything.
| Rabbit urine + EM4 + aeration[5] | |||
| aeration time | 0 hour | 48 hours | 96 hours |
| pH | 6.63 | 9.76 | 10.20 |
| C-Organic | 2.40 | 2.63 | 2.62 |
| N | 2.26 | 2.19 | 2.44 |
| C/N Ratio | 1.06 | 1.19 | 1.07 |
Look at the organic c. After being aerated for 96 hours (4 days) nothing happened to the organic c.
This means that the bacteria contained in em4 are not working properly. Namely decomposing organic compounds found in rabbit urine.
As a result, the organically bonded N does not escape. So that it also resulted in no increase in its N value.
If you want to aerate, the bacteria used should be Nitrobacter and Nitrosomonas.
Nitrobacter and Nitrosomonas will produce nitrites and nitrates which are needed by plants.
Reference
[1] Sembiring, Melda Yuartaria, Lilik Setyobudi and Yogi Sugito. Effect of Rabbit Urine Dosage on Growth and Yield of Several Tomato Varieties. Department of Agricultural Cultivation, Faculty of Agriculture, Brawijaya University. Journal of Plant Production Vol. 5 No. 1, January 2017.
[2] Fitriasari. Chintia, and Erlina Rahmayuni. The Effectiveness of Giving Rabbit Urine To Reduce The Dose Of Inorganic Fertilizer In Sweet Corn Cultivation. Faculty of Agriculture, University of Muhammadiyah Jakarta.
[3] Prabowo, Inggi. 2017. The Effect of Differences in Feed Ration on Macro Nutrient Levels (NPK) in Rabbit Urine. Biology Education Study Program, Teaching and Education Faculty, Universtas Nusantara PGRI Kediri.
[4] Azizah, Nur. 2017. The Effect of Decomposer Type and Long Fermentation on the Quality of Rabbit’s Liquid Fertilizer (Biourine). Thesis. Faculty of Animal Husbandry Hasanuddin University Makassar.
[5] Rasyid, Rismawati. 2017. Quality of Rabbit’s Liquid Fertilizer (Biourine) Produced Using Different Types of Decomposers and Aeration Process Time. Thesis. Animal Husbandry Study Program, Faculty of Animal Husbandry, Hasanuddin University Makassar.
[6] Fithriani. Pipit, Dadan Ramdani Nugraha and Umar Dani. The Effect of Doses of Inorganic Fertilizers and Moles (Local Microorganisms) on the Growth and Yield of Rice Plants (Oryza Sativa L.) Kulivar Inpari 30. Agrotechnology Study Program, Faculty of Agriculture, Majalengka University.
[7] Magfiroh. Lilia Seldon and Wahyu Indra Duwi Fanata. 2017. IbM Farmers Group in Semboro Subdistrict, Jember Regency, Through Technology Transfer Using Rabbit Urien Waste Into Organic Pesticides and Organic Fertilizers to Increase Production of Agricultural Products. Science and Technology Report for the Community (IbM). # hydroponics #Universitas Jember.
 JOYNIM FARM Goat Farming, Cattle Farm, Laying Hens, Quail Farm, Gardening
JOYNIM FARM Goat Farming, Cattle Farm, Laying Hens, Quail Farm, Gardening