Corn plants are common to be used as animal feed. Livestock such as cattle, goats, or sheep usually like these corn crops.
This is because the part of the corn plant has a pretty good palatability.
Almost all parts of this plant indeed can be used for animal feed.
Indeed, most of which are used as an animal feed is the leaves and stems.
However, still there are other parts that can be utilized. That is corn husk. This will be the focus of our discussion.
The leaves and stems of corn after harvesting will have a low economic value.
Despite its low economic value, corn forage among the lower farmer is expensive.
Supposedly, as much as possible the feed should not be bought. Moreover, for breeders that have livestock for one or two head only.
However, different regions differ in price.
There are areas that are indeed high maize production. There are also areas where its agriculture is economically less valuable when planted with corn.
Thus, the price of corn forage is heavily influenced by a little bit of stock in the region.
Back to the corn husk. There is a study of the students of one state university in Solo, Central Java, Indonesia.
The research was conducted in 2010. Long enough, but it’s okay hopefully can still be an insight and reference.
His research is about using corn husk to be given to sheep.
Corn husk is given in varying amounts ranging from without husk until the number of corn husk in the ration is as much as 70%.
This becomes interesting because of the amount of corn husk given up to that much.
Is the amount of corn husk as much as this can give a positive impact or vice versa?
Keep continue reading to find out the information.
Nutritional content of cornhusk
What is the nutritional content of cornhusk?
The nutritional content of cornhusk according to the results of proximate analysis of laboratory cattle feed, Grati, Pasuruan, East Java are: dry matters 42.56%, crude protein 3.4%, fat 2.55%, crude fiber 23.318% and TDN 66.41%.
When compared with water hyacinth, as in my previous post, corn husks has a fairly high dry matter. However, the crude protein content is less.
Hyacinth has very little dry matter, but in the dry matter content, the crude protein is tolerable.
Corn husk research
The way this research is done briefly I will describe.
All the tools and cages cleaned. The sheep that will be used as research livestock cleared from the parasite and then preparing for ration that will be made in research.
Cleaning the cages and equipments
Sheep cages and the all equipments before use is cleaned first to prevent the development of pathogenic microbes that can interfere with health.
The sheep cages were diliscected by using Lysol at a dose of 15 ml / 10 liters of water.
Place foor feed and drink and other equipment washed with soap and soaked with Lysol antiseptic with dosage of 15 ml / 10 liters of water. Then dried and put in a cage.
Cleaning the parasites on goats and sheep
Sheep before being fed the treatment, it were given Nemasol worm medicine with a dose of 375 mg / 45 kg BB.
The goal is to remove parasites in the digestive tract.
Preparation of sheep done for 2 weeks for adaptation to the environment of the cage and feed.
The 12 sheep were divided into 3 treatment groups, each treatment group consisted of 4 replications, and each repetition consisted of 1 sheep.
Making concentrate and corn husk silage
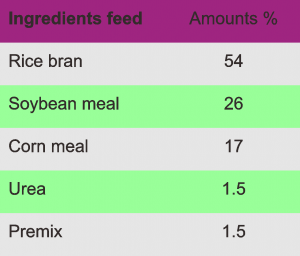
The concentrate is made by selfmixing. The ingredients consists of rice bran, soybean meal, corn flour, urea and premix.
While silage is made from corn husk. The trick is corn husks cut into pieces between 3 – 5 cms and then dried to a moisture content of about 50%..
After that, mixed with molasses as much as 4% until evenly distributed. Then wrapped tightly with plastic bags and stored for 21 days.
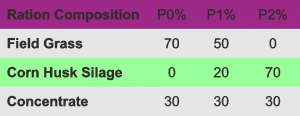
The ration composition used in this study is divided into three kinds.
First, sheep were fed a ration consisting of 70% of the field grass, 30% concentrate, without the silage of corn husks.
Second, sheep fed a ration consisting of 50% of field grass, 30% concentrate and 30% silage of corn husks.
Third, sheep are fed a ration consisting of 30% concentrate, 70% silage of corn husks and no field grass at all.
One of the objectives of this research is to find out whether the corn husks silage can replace the whole field grass.
Later, we can see the results .
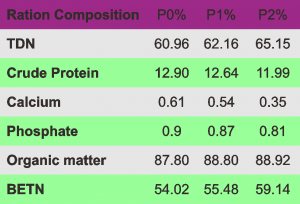
The research is fairly complete, so it makes it easy to understand. Included also the nutritional content of the three rations. The data can be seen in the table below.
The nutrient content of each ration is shown in the table below.
PO is the first ration, P1 is the second sheep ration, and P2 is the third ration of sheep feed.
All three have similar nutritional content, although there are differences in nutritional value, but the value is very small.
Concentrates used for sheep, the composition can be seen in the table below.
Results
The results of this study are very positive. Positive for small-scale farmers (like me).
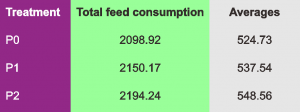
As shown in the table, sheep fed without corn husks silage, the average daily consumption was 524,73 grams/day.
Sheep fed ration containing 20% silage of corn husks (P1), the average consumption of sheep as much as 537, 54 grams/head/day.
While sheep fed rations containing 70% silaged corn husks (P2), the average consumption of sheep as much as 548.56 grams/head/day.
When examined from these results, the replacement of corn husks silage for field grass did not give a negative effect on the consumption of rations.
The amount of ration consumption even tends to increase with the addition of silage klobot corn.
So, it does not matter if the sheep are fed with silage of corn husks and concentrate even without other forage.
Here, the corn husks silage can replace the grass field and its palatability is also as good as the grass of the field.
However, the silage of corn husks is given in the form of silage.
In the scale of research, the feeding of silage is also not in a long time.
After the research is done, it usually ends …
Not tested for long-term giving.
Although in the scale of the study, giving a full ration of corn husks silaged and concentrate is successful. Although for long-term use it still needs to be careful. That’s my opinion.
For additional information, this study lasted for 10 weeks or about 2 months and a half.
So, to be used as seasonal feed, may be it still possible if only 10 weeks.
If you have to store corn husks and will be used long term, a year for example, it seems to need to be studied further. Or consult it to the experts or experienced breeders.
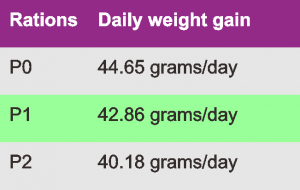
The next result is the increase of daily weight of the sheep that are fed this corn husks ration.
Livestock hooked eat is not enough, if eating a lot but not make weight gain is useless.
Therefore, I show the result of weight gain of sheep body by feeding ration of corn husk silaged.
The results are presented in the table and can be seen below.
Sheep that only given concentrate and field grass rations (P0), the average daily weight gain is 44.65 grams / day.
For sheep ration with 20% of corn husks silaged (P1), body weight gain is 42,86 gram / day.
While the sheep that were given rations with corn husks silaged up to 70% (P2), Daily weight gain is 40.18 grams / day.
The increase of body weight of research sheep decreased with increasing number of corn husks silaged.
Although the difference in weight gain is not much, researchers consider this does not matter.
Silage of corn husks is still Ok to use as a substitute for grass field. I myself also agree with that.
Reference
Purwanto. 2010. Influence of Corn Silage Leather In Appearance on Diet Local Production of Male Sheep. Faculty of Agriculture Sebelas Maret University Surakarta.
 JOYNIM FARM Goat Farming, Cattle Farm, Laying Hens, Quail Farm, Gardening
JOYNIM FARM Goat Farming, Cattle Farm, Laying Hens, Quail Farm, Gardening





The leaves and stems, in particular, are commonly used as animal feed. However, there are still certain parts that can be used. Thank you for sharing this information!